eCommerce Website
eCommerce has completely changed how we buy and sell goods in the modern day. E-commerce has become a major force in the global economy thanks to the quick development of technology and the growing...

eCommerce has completely changed how we buy and sell goods in the modern day. E-commerce has become a major force in the global economy thanks to the quick development of technology and the growing connectivity of people throughout the world.
This blog post will examine the constantly changing e-commerce landscape, its effects on businesses and customers, and the major themes influencing its future.
What is eCommerce?
The exchange of goods, services, or information through the Internet or other electronic networks is referred to as "e-commerce" or "electronic commerce." Using digital platforms for different business processes, including marketing, sales, payment processing, and customer support, entails carrying out commercial transactions online.
E-commerce refers to the exchange of goods, services, or information between companies and customers over the Internet using digital technologies. Online marketplaces, business-to-business exchanges, online retail stores, and online auctions are just a few examples of the different ways that e-commerce can be conducted. It makes physical storefronts unnecessary and makes it possible for companies to reach clients all over the world.
What is an eCommerce Website?

An e-commerce website serves as your online storefront. It simplifies the transaction process between buyers and sellers by providing an online platform where products are showcased and customers can make their selections. Your website serves as the virtual counterpart to the product racks, salespeople, and cashiers found in traditional commerce.
Businesses have the option to develop their own e-commerce website on a dedicated domain, establish a branded store experience on platforms like FossTechUzon, and Amazon, or pursue a multi-channel approach to encompass all possibilities.
How does eCommerce Work?
E-commerce is the process of purchasing and selling goods and services online using digital technologies and online distribution channels. The typical procedure consists of the following steps:
- Establishing an eCommerce Website or Platform: A business creates an eCommerce website or platform to display its goods and services. This entails creating a user-friendly interface, adding important functions, and guaranteeing a safe online setting.
- Product Catalog Creation: The company compiles a list of all of its products into a catalog that includes specifics such as product descriptions, photos, costs, and variations. This catalog has been added to the online store.
- Online Product Display: Users browse the offered goods and services on the eCommerce website. They can use filters, browse through categories, look up specific things, and view product details.
- Product Selection and Shopping Cart: Customers choose the desired products and add them to a virtual shopping cart after making their selections. Customers can examine, edit, or remove goods from their shopping basket as needed. The shopping cart keeps track of the items they have chosen.
- Secure Checkout Process: When clients are prepared to make a purchase, they move on to the secure checkout process. This includes supplying shipment details, choosing a payment option, and verifying the order specifics.
- Payment Processing: The e-commerce platform integrates secure payment gateways that handle online payment transactions. Customers can make payments using credit cards, debit cards, digital wallets, or other available payment options.
- Order Confirmation: Once the payment is successfully processed, the customer receives an order confirmation, which includes details such as order number, purchased items, shipping information, and estimated delivery time.
- Order Fulfillment and Shipping: The business prepares the order for shipment. This involves picking the products from inventory, packaging them securely, and generating shipping labels. The order is then handed over to the logistics provider for delivery.
- Shipment Tracking: Customers can track the status of their shipments through tracking numbers provided by the logistics provider. They receive updates on the whereabouts of the package until it reaches the designated delivery address.
- Customer Support and After-Sales Service: Throughout the process, the e-commerce website provides customer support channels, such as live chat, email, or phone, to address inquiries, resolve issues, and provide assistance. After-sales service may include handling returns, exchanges, or addressing customer concerns.
- Data Analysis and Optimization: eCommerce platforms collect information about customer behavior, past purchases, and other variables. This data is analyzed to gather insights, improve marketing tactics, improve user experience, and promote business growth.
It's vital to remember that based on the eCommerce platform, business strategy, and industry, the particular phases and processes may change. However, utilizing digital technologies to facilitate frictionless online transactions between firms and customers is the core idea behind eCommerce.
What are the Types of eCommerce?
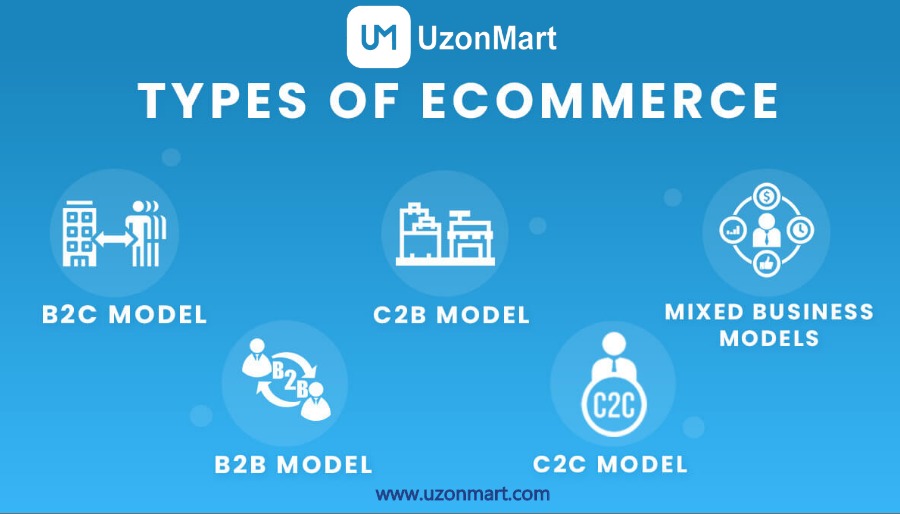
eCommerce, also known as electronic commerce, pertains to the online exchange of goods and services. It encompasses various models, each distinguished by its distinct characteristics. Here are some common types of eCommerce:
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C): This is the most well-known type of E-commerce, where businesses sell products or services directly to individual consumers. Examples include online retail stores, such as FossTechUzon LLP, Amazon, or Walmart online store, where consumers can purchase products directly from the website.
- Business-to-Business (B2B): Within this model, businesses engage in selling products or services to fellow businesses. It involves transactions between manufacturers, wholesalers, and retailers. B2B eCommerce platforms facilitate bulk orders, supply chain management, and streamlining business processes. An example, such as UzonMart, is a website where manufacturers sell products in bulk to retailers.
- Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C): C2C eCommerce facilitates transactions among individual consumers. These platforms provide a marketplace where individuals can buy and sell products or services to each other. Popular C2C platforms include eBay and Craigslist, where people can list items for sale and make transactions directly with other individuals.
- Consumer-to-Business (C2B): In this model, individuals sell products or services to businesses. It typically involves freelancers or independent professionals offering their services to companies. For example, a freelance writer offering content writing services to various businesses through online platforms.
- Business-to-Administration (B2A): B2A eCommerce encompasses transactions between businesses and governmental entities or administrations. It encompasses online transactions between companies and government agencies, such as businesses paying taxes or submitting electronic bids for government contracts.
- Consumer-to-Administration (C2A): C2A eCommerce involves transactions between individuals and government entities or administrations. It includes online interactions between citizens and government agencies, such as paying taxes or renewing driver's licenses through government websites.
These are general categories, and these models can be variations and combinations in the rapidly evolving world of eCommerce. Some businesses may operate in multiple models simultaneously or employ a hybrid approach to suit their specific needs.
Features of an eCommerce Website

Product Catalog: An eCommerce website includes a comprehensive catalog of products or services. Each item is typically accompanied by detailed information, including descriptions, images, pricing, and variations (such as size, color, or quantity).
- Shopping Cart: eCommerce websites incorporate a shopping cart feature that allows customers to select multiple items for purchase. The shopping cart keeps track of the selected products and enables customers to review, modify, or remove items before proceeding to checkout.
- Secure Payment Gateway: eCommerce websites integrate secure payment gateways to facilitate online transactions. These gateways enable customers to make payments using various methods, such as credit cards, debit cards, digital wallets, or alternative payment options.
- User Account Management: eCommerce websites often provide user account functionality, allowing customers to create and manage their profiles. User accounts enhance the shopping experience by enabling features such as saved addresses, order history, wish lists, and personalized recommendations.
- SEO Function: eCommerce websites provide efficient search functionality and robust filtering options to enable customers to find specific products quickly. By incorporating targeted keywords and implementing effective search engine optimization strategies, businesses can enhance their website's visibility, attract organic traffic, and improve the overall user experience.
- Order Management: eCommerce websites incorporate order management systems to handle the processing and fulfillment of customer orders. This includes generating order confirmations, tracking shipment status, and managing returns or exchanges.
- Customer Reviews and Ratings: Many eCommerce websites feature customer reviews and rating systems. These allow customers to provide feedback on products and share their experiences, helping other potential buyers make informed decisions.
- Responsive Design: Given the increasing use of mobile devices for online shopping, eCommerce websites often employ responsive design. This ensures that the website adapts and provides an optimal browsing experience across various screen sizes and devices.
- Analytics and Reporting: eCommerce websites integrate analytics tools to track and analyze user behavior, sales data, and other key metrics. This information helps businesses gain insights into customer preferences, optimize marketing strategies, and improve overall performance.
- Security Measures: eCommerce websites prioritize security to protect customer information and ensure safe online transactions. They implement security measures, such as SSL encryption, secure data storage, and compliance with data protection regulations.
eCommerce websites play a critical role in enabling businesses to establish an online presence, reach a global customer base, and conduct transactions efficiently. They provide a user-friendly interface, seamless shopping experience, and essential features to support the entire eCommerce process, from product discovery to order fulfillment.
Benefits of eCommerce
eCommerce offers numerous benefits for businesses, consumers, and the overall economy. Here are some key benefits of eCommerce:
- Global Reach: eCommerce breaks down geographical barriers, allowing businesses to reach a global customer base. With an online store, businesses can expand their market reach beyond local or regional boundaries, potentially accessing millions of potential customers worldwide.
- 24/7 Availability: Unlike physical stores with fixed operating hours, eCommerce websites can operate 24/7. Customers have the flexibility to browse and make purchases at their convenience, which increases accessibility and allows businesses to generate sales even outside regular business hours.
- Lower Operational Costs: Running an online store often incurs lower operational costs compared to brick-and-mortar establishments. eCommerce eliminates the need for physical shops, lowering employee, rent, and utilities costs. Additionally, online inventory management and automated order processing can streamline operations and reduce labor costs.
- Increased Customer Convenience: eCommerce offers customers the convenience of shopping from anywhere at any time. They can browse products, compare prices, and make purchases with just a few clicks. This convenience factor contributes to customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Expanded Product Selection: Online stores can offer a vast range of products compared to physical stores constrained by shelf space. eCommerce allows businesses to showcase an extensive inventory, providing customers with more choices and increasing the likelihood of finding the desired products.
- Personalization and Targeted Marketing: eCommerce platforms can collect and analyze customer data, allowing businesses to personalize the shopping experience. By tracking customer preferences and behavior, businesses can offer tailored product recommendations, targeted promotions, and personalized marketing campaigns, increasing the likelihood of conversion and repeat purchases.
- Cost-Effective Marketing and Advertising: Digital marketing strategies, such as search engine optimization (SEO), social media marketing, and email marketing, can be more cost-effective compared to traditional advertising methods. Online marketing allows businesses to target specific customer segments and track the effectiveness of their campaigns in real time.
- Improved Customer Insights: eCommerce platforms provide businesses with valuable data and analytics. They can track customer behavior, purchase history, and preferences, enabling businesses to gain insights into customer preferences, refine their marketing strategies, and make data-driven decisions to optimize their offerings.
- Streamlined Inventory Management: eCommerce systems integrate inventory management, allowing businesses to track stock levels in real time. This helps optimize inventory turnover, reduce the risk of stockouts or overstocking, and automate reordering processes, leading to improved efficiency and cost savings.
- Efficient Order Fulfillment: eCommerce allows for streamlined order processing and fulfillment. Businesses can automate order confirmation, shipping notifications, and tracking updates, providing customers with a seamless and transparent purchasing experience. This efficient order fulfillment contributes to customer satisfaction and loyalty.
These benefits make eCommerce a powerful tool for businesses to expand their reach, increase sales, and enhance customer experiences in the digital age.
Types of eCommerce Revenue Models

There are several types of revenue models commonly used in eCommerce. Here are some of the most popular ones:
- Sales Revenue Model: This is the most basic revenue model where the eCommerce company generates revenue by selling products or services directly to customers. The company earns money by setting prices for its products or services and making a profit from the sales.
- Subscription Revenue Model: In this model, the eCommerce company charges customers a recurring fee in exchange for access to certain products or services. Examples include subscription boxes, streaming services, or membership-based e-commerce platforms.
- Advertising Revenue Model: eCommerce companies can generate revenue by displaying advertisements on their website or platform. They earn money by charging advertisers for ad space or based on the number of clicks or impressions the ads receive.
- Affiliate Revenue Model: With this model, the eCommerce company earns a commission by promoting and selling products or services from other companies. The company acts as an intermediary between the customer and the merchant, earning a percentage of the sale price for each successful referral.
- Freemium Revenue Model: In the freemium model, the eCommerce company offers basic services or products for free but charges for additional features, premium content, or advanced functionalities. The idea is to attract a large user base with the free offering and then convert a portion of those users into paying customers.
- Dropshipping Revenue Model: Dropshipping involves selling products online without physically stocking them. Instead, the e-commerce company partners with suppliers who handle inventory management and shipping. The company earns revenue by marking up the price of the products it sells and keeping the difference between the supplier's price and the selling price.
- Marketplace Revenue Model: eCommerce marketplaces earn revenue by charging fees or commissions on transactions that occur between buyers and sellers on their platform. They may charge a percentage of the sale price, a flat fee per transaction, or a subscription fee for sellers to access the marketplace.
- Data Monetization Revenue Model: Some eCommerce companies collect user data and analyze it to gain insights or sell it to third parties, such as advertisers or researchers. They generate revenue by leveraging the data they gather through their platform.
These are just a few examples of revenue models in eCommerce, and companies often use a combination of these models or create innovative variations to suit their specific business goals.
Example of eCommerce

They are FossTechUzon (India) LLP, a reputable website design and software development company established in 2019. It was founded by Mohd Salman Khan. They specialize in Developing eCommerce websites that are specifically designed to fulfill the demands of companies vying for online success. Their comprehensive offerings include B2B Portal Development, Software Development, ERP Solutions, CRM Implementation, Attendance Management Systems, and more. At FossTechUzon, they firmly believe in cultivating strong and collaborative partnerships with their clients, enabling them to gain deep insights into their specific needs. This allows them to craft customized strategies that align perfectly with their business objectives. Their exceptional track record of delivering successful outcomes has earned the trust and confidence of clients, who rely on them to help them achieve their online goals. They invite you to reach out to them today to discover more about their services and how they can play a pivotal role in facilitating the growth and success of your business.
Conclusion
E-commerce has come a long way since its inception, transforming the retail landscape and providing endless opportunities for businesses and consumers alike. The evolution of technology, changing consumer behaviors, and innovative business models continue to shape the future of e-commerce. To thrive in the dynamic digital marketplace, businesses must continuously adapt to the evolving landscape, embrace emerging technologies, and prioritize customer-centric strategies as they move forward.
Your feedback matters to us at UzonMart! Share your experiences by posting a review on our website. Your valuable feedback helps others make informed choices. We appreciate your decision to choose our services and value the feedback you provide. Thank you for providing us with the opportunity to enhance our service to you.
Pricing
Category
Website DesignInterested in eCommerce Website?
Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you with eCommerce Website.
Get In Touch

